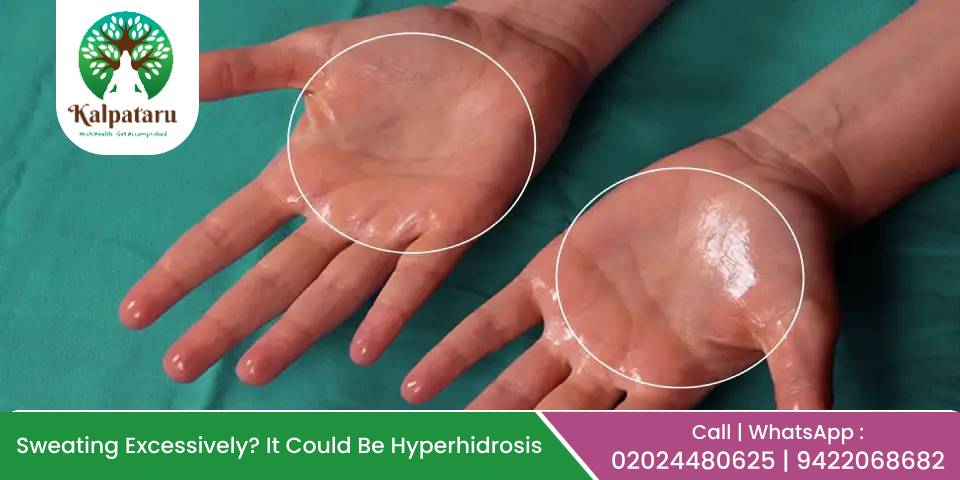
Sweating is a natural and essential function of the body that helps regulate temperature and expel toxins. However, some people experience excessive sweating even when they are not in a hot environment or physically active. This condition, known as hyperhidrosis, can significantly impact daily life, making simple tasks like shaking hands, writing, or holding objects uncomfortable and embarrassing.
Understanding Hyperhidrosis:
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating beyond what is necessary for body temperature regulation. It commonly affects areas such as the palms, feet, underarms, and face. It can be classified into primary hyperhidrosis, which has no underlying medical cause and is often hereditary, and secondary hyperhidrosis, which is linked to medical conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, obesity, and infections. Studies show that about 5% of the global population suffers from hyperhidrosis, yet many cases remain undiagnosed and untreated. Additionally, around 30-50% of individuals with hyperhidrosis have a family history of the condition, suggesting a strong genetic component.
Causes and Triggers of Hyperhidrosis:
Causes of Hyperhidrosis:
Hyperhidrosis occurs due to an overactive sympathetic nervous system that overstimulates the sweat glands. The causes can be classified into primary and secondary factors:
- Primary Hyperhidrosis: This type occurs without any underlying medical condition and is typically hereditary. It usually begins in childhood or adolescence and affects specific areas like the hands, feet, underarms, and face.
- Secondary Hyperhidrosis: This type is triggered by an underlying medical condition or external factors. It often causes excessive sweating over larger areas of the body and may develop later in life. Common causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like hyperthyroidism or menopause can lead to increased sweating.
- Neurological Disorders: Diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and stroke can cause excessive sweating.
- Infections: Tuberculosis, malaria, and other infections can lead to profuse sweating.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including antidepressants, pain relievers, and some diabetes medications, can trigger excessive sweating.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can increase sweating due to higher metabolic activity and heat retention.
- Anxiety and Stress: Emotional distress can overstimulate sweat glands, leading to excessive sweating episodes.
Modern Medical Treatments for Hyperhidrosis:
There are several modern treatment options available for managing hyperhidrosis effectively. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on daily life. Some commonly used medical treatments include:
- Antiperspirants: Prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can help block sweat ducts and reduce excessive sweating, especially in the underarm area.
- Medications: Oral medications such as anticholinergics can help reduce sweat production by blocking nerve signals to the sweat glands.
- Botox Injections: FDA-approved botulinum toxin (Botox) injections temporarily block the nerves that stimulate sweat glands, providing relief for several months.
- Iontophoresis: This treatment uses a mild electrical current to temporarily disable sweat glands, particularly useful for excessive sweating of the hands and feet.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) may be performed to sever nerves responsible for excessive sweating. However, surgery is generally considered a last resort due to potential side effects.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Excessive Sweating:
Excessive sweating (Atisweda) in Ayurveda is associated with an imbalance of Pitta dosha and the accumulation of Kledha (moisture retention in the body). Factors such as excessive Ama (toxins), increased Medha dhatu (fat tissue), and obesity can contribute to excessive perspiration. When Pitta becomes aggravated due to factors like excessive heat, spicy foods, stress, or hormonal imbalances, it increases internal body heat, leading to excessive sweating. Ayurveda considers hyperhidrosis as Atisweda, a condition that requires balancing the body’s heat and internal energy flow.
Ayurvedic Remedies for Hyperhidrosis:
Ayurveda offers holistic and natural ways to manage hyperhidrosis by cooling the body and restoring balance to the Pitta dosha. Some effective Ayurvedic remedies include:
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding spicy, fried, and excessively salty foods can help reduce body heat.Avoid late night food & irregular sleep patterns. Consuming cooling foods such as salads, black raisins, figs, kokum, lemon-based drinks, cucumber, watermelon, buttermilk, and coconut water helps balance Pitta.
- Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic herbs like Shatavari, Amla, Ushir, Sariva , Musta,Sandalwood, and Neem have cooling properties that help regulate excessive sweating and detoxify the body. Amapachak medicines Help in digestion and toxin removal. Formulations like Chaturthaka help regulate fat metabolism. Vanga Bhasma is beneficial in controlling excessive sweating. Ayurvedic Siddha-jala (medicated water) prepared with Vala, Pittapapada, Chandan (red sandalwood), and Nagarmotha.
- Stress Management: Since stress and anxiety can worsen hyperhidrosis, Ayurveda emphasizes yoga, meditation, and Pranayama (breathing exercises) to calm the nervous system and control sweating.
- Natural Deodorants and Topical Applications: Applying sandalwood powder, rose water, or Multani mitti (Fuller’s earth) to the affected areas helps absorb excess sweat and reduce body odor naturally.
- Panchakarma Detoxification: Shirodhara and Takradhara helps to Calm the nervous system and reduce excessive sweating. Virechana & Abhyanga Therapy Eliminates excess body heat and balances Pitta dosha.
- Clothing & Lifestyle Changes: Wear breathable cotton clothing to allow proper ventilation and prevent sweat retention. Avoid synthetic fabrics, especially for innerwear like underwear and vests, to reduce discomfort caused by excessive sweating.
- External Application: Udwarthana (Herbal Powder Massage) Using Triphala, Nagarmotha, and Pittapapada in an Udwarthana (dry powder massage) can open skin pores and allow sweat release, helps to balance Pitta dosha, reducing excessive sweating. In cases of excessive scalp and forehead sweating while eating, applying Lodhra and Vala paste can help regulate overactive sweat glands (Sweda Granthi).
Get Ayurvedic Solutions at Kalpataru Ayurvedic Clinic™:
If excessive sweating is interfering with your daily life, Ayurveda offers natural and effective treatments to restore balance and well-being. At Kalpataru Ayurvediya Chikitsalaya™ Pune, we provide personalized Ayurvedic solutions tailored to your body’s needs. With over 25 years of experience, our expert team helps patients manage hyperhidrosis through holistic therapies, herbal treatments, and lifestyle modifications.
Don’t let excessive sweating control your life! Book a consultation today and experience the benefits of Ayurveda in managing hyperhidrosis naturally.