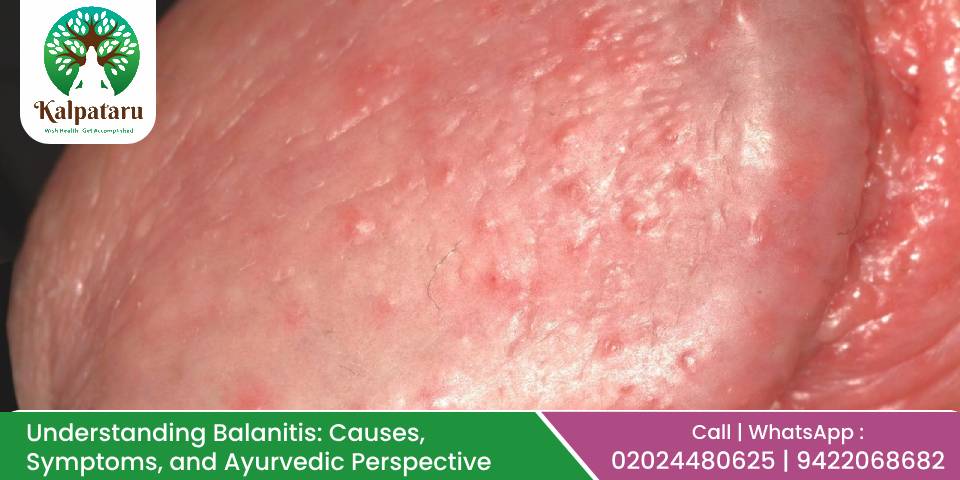
Balanitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the glans penis, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and discomfort. While commonly affecting uncircumcised males, it can occur in anyone with a penis. This blog explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how Ayurveda provides a unique perspective on managing balanitis.
What is Balanitis?
The term “balanitis” comes from the Greek word balanos, meaning “acorn,” which refers to the shape of the glans penis. This condition is not only uncomfortable but can sometimes lead to complications if untreated.
Causes of Balanitis:
Several factors contribute to balanitis, including:
- Poor Hygiene: Accumulation of smegma (a combination of shed skin cells, oils, and moisture) can lead to irritation and infection.
- Infections:
- Bacterial: Staphylococcus or Streptococcus species.
- Fungal: Candida albicans is a common culprit.
- Viral: Herpes simplex virus in some cases.
- Allergic Reactions: Reaction to soaps, detergents, or latex condoms.
- Irritation: Use of scented hygiene products or tight-fitting clothing.
- Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes mellitus (increases the risk of fungal infections).
- Autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms of Balanitis:
- Redness and swelling of the glans penis.
- Pain or discomfort, especially during urination or sexual activity.
- Foul-smelling discharge.
- Itching or burning sensation.
- Difficulty retracting the foreskin in severe cases (phimosis).
Conventional Treatments for Balanitis:
- Hygiene: Regular cleaning with warm water and gentle soap.
- Topical Medications:
- Antifungal creams (e.g., clotrimazole) for fungal infections.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Corticosteroid creams for inflammation if not responding to conventional treatment.
- Avoiding Irritants: Discontinuing use of scented products, soaps or allergenic materials.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Controlling blood sugar in diabetic patients.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Balanitis:
In Ayurveda, balanitis can be understood as a condition caused by an imbalance in the kaf and Pitta Dosha, which governs fluid balance, heat and inflammation in the body. The aggravated Pitta, along with Kapha Dosha (responsible for moisture and accumulation), can lead to symptoms akin to balanitis.
Ayurvedic Causes and Pathogenesis:
- Dietary Factors: Excess consumption of spicy, acidic, or salty foods aggravates Pitta Dosha.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor hygiene, lack of cleanliness, eating food items agreveting kaf dosh such as dairy products, sugary food,and excessive sweating contribute to Kapha imbalance.
- Infections: Could be linked to Krimi (microbial pathogens) in Ayurveda.
Ayurvedic Management of Balanitis:
Herbal Remedies:
- Neem (Azadirachta indica): Known for its antibacterial and antifungal properties. Neem paste or decoction can be applied locally.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): A natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial. A paste made with turmeric and water can soothe irritation.
- Aloe Vera (Kumari): Provides a cooling effect and reduces inflammation.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Include cooling foods like cucumber, watermelon, and coconut water to pacify Pitta.
- Avoid spicy, salty, and fermented foods that exacerbate heat.
Detoxification: Panchakarma therapies like Virechana (purgation) may be recommended to eliminate excess Pitta.
Hygiene and Local Applications:
- Wash the affected area with decoctions of Triphala or Vetiver (Ushira) to cleanse and soothe the glans.
- Avgah chiktsa- immersing penis in a medicated decoration prepared by using some herbs like Vara gives very quick relief from balanitis.
- Creams – various ayurvedic creams prepared with purified sulfer have great role in Ayurveda regarding cure of balanitis
- Use herbal oils like Jatyadi Taila for wound healing and infection prevention.
Internal Medications:
- Herbs like Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia) and Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia) to purify the blood and reduce inflammation.
- Chandraprabha Vati, trivang bhasms for managing infections and maintaining urinary tract health.
Lifestyle Modifications in Ayurveda:
- Maintain proper hygiene, especially after urination or sexual activity.
- Wear loose, breathable clothing made of natural fabrics like cotton.
- Avoid excessive heat and sweating, as it aggravates Pitta Dosha.
When to Consult a Doctor?
While mild cases of balanitis may resolve with improved hygiene, persistent or severe symptoms require medical attention. Delayed treatment can lead to complications like:
- Phimosis.
- Recurrent infections.
- Scarring.
Conclusion:
Balanitis, though a common condition, can be effectively managed with proper care. Ayurveda offers a holistic approach by addressing the root causes, pacifying dosha imbalances, and promoting long-term health. Combining Ayurvedic remedies with modern hygiene practices can lead to quicker recovery and prevent recurrences.
In Kalpataru Ayurvediya Chikitsalaya™ so many patients of chronic recurrent balanitis patients have been cured who were otherwise advised to undergo circumcision surgery.
Dr. Manoj Deshpande and Dr. Aparna Deshpande at Kalpataru Ayurvediya Chikitsalaya™ Clinic provide the best Ayurvedic Treatment for Psoriasis & various diseases in Pune, Maharashtra. For more information about our comprehensive treatment options, or to requestan appointment with the best Ayurvedic Doctor in Pune, call +919422068682 / +919764837167 / 020-24480625 or Click on Book an Appointment.